Pan, Zoom and Orbit Behavior (Unity)
UI elements to Orbit, Zoom, Pan and Reset View. GUIs to tweak values for demo purposes.
Source Code
References
Table of Content
- Source Code
- References
- Table of Content
- Final Result
- Input Actions
- On Screen Controls
- Connecting to the CameraMovement
- GUIs for Playground
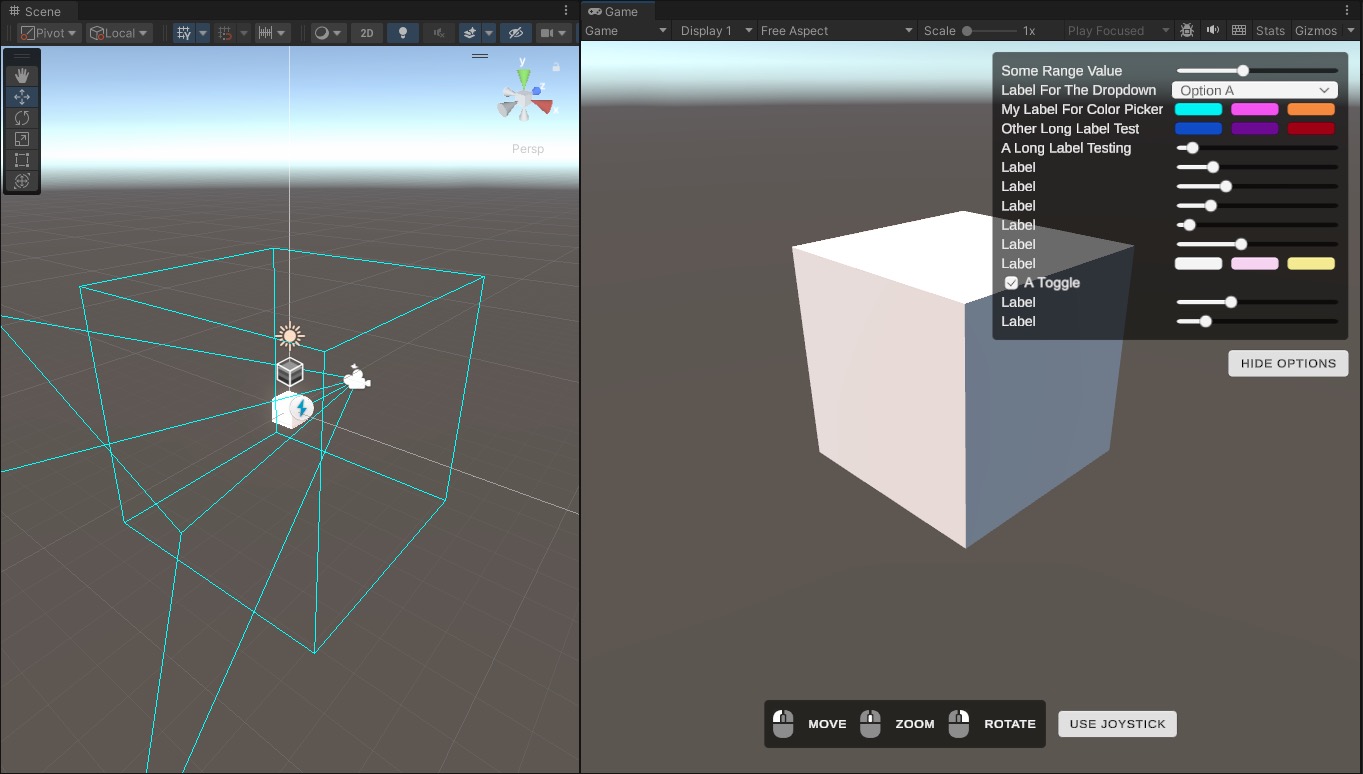
Final Result
A demo scene with view control to navigate the scene, and a playground to tweak values in the demo.
Input Actions
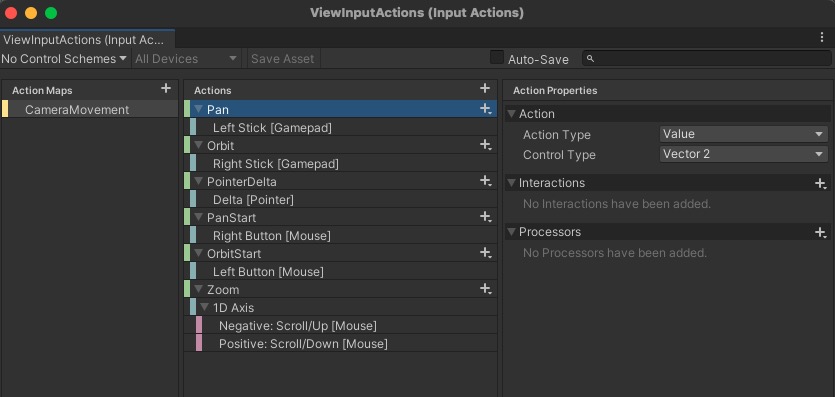
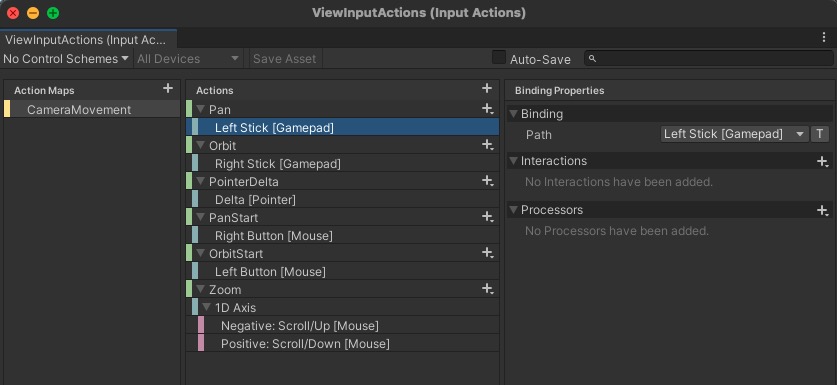
Using the Input System Package from Unity, create an Input Actions asset and setup the Action Maps.
- Orbit and Pan will be
Action Typeset toValue, because we want the actualVector2coming from the analog stick on screen. - The
Control Typewill be set toStick, so we can bind it to theGamepad Stick. - The
Bindingwill be set to theLeft StickandRight Stick, correspondingly.
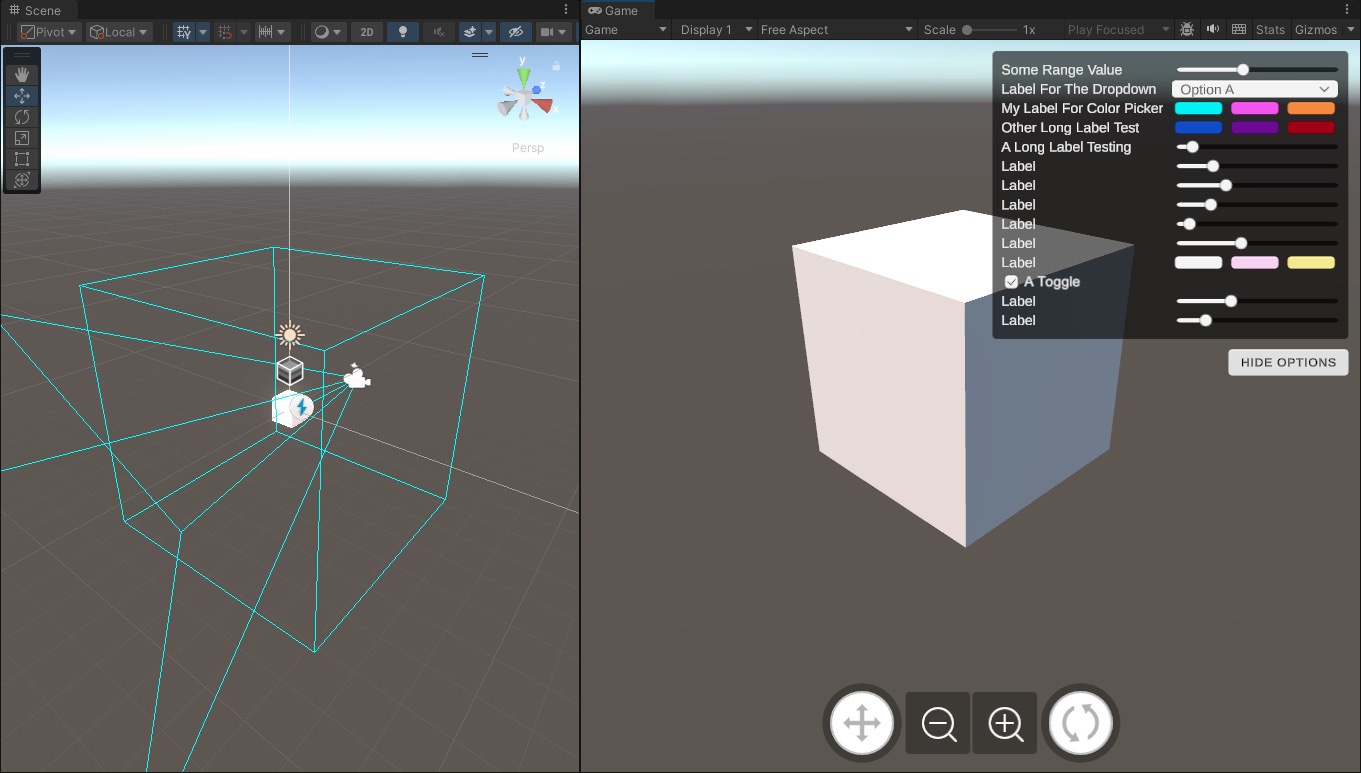
On Screen Controls
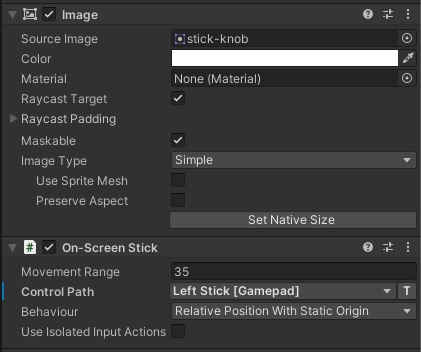
We will need to add Unity UI Game Objects to represent the analog sticks on the screen.
- Adding the built in
On-Screen Stickbehavior to the image component will do it. - We need to set the
Control Pathof the on screen stick toLeft Stick [Gamepad]andRight Stick [Gamepad]correspondingly.
Connecting to the CameraMovement
- The
CameraMovementclasses will listen to events such asOnPanorOnPointerDelta. - And internally will use these inputs to move the camera accordingly.
Input Signals
1private void OnPan(InputValue value) => panAmount = value.Get<Vector2>(); 2private void OnOrbit(InputValue value) => orbitAmount = value.Get<Vector2>();
1private void OnPointerDelta(InputValue value) 2{ 3 orbitAmount = isOrbiting ? value.Get<Vector2>() : Vector2.zero; 4 panAmount = isPanning ? value.Get<Vector2>() * -1.0f : Vector2.zero; 5} 6 7private void OnOrbitStart(InputValue value) 8{ 9 isOrbiting = value.isPressed; 10} 11 12private void OnPanStart(InputValue value) 13{ 14 isPanning = value.isPressed; 15} 16 17private void OnZoom(InputValue value) 18{ 19 zoomAmount = value.Get<float>(); 20}
Pan View
- Given the
Vector2amount of movement from the analog stick, we move the camera along itsup/downandright/leftdirections. - We also reposition the orbit pivot, which will be used later for orbiting around it.
1private void HandlePan() 2{ 3 if (panAmount == Vector2.zero) { return; } 4 5 var direction = camera.transform.right * panAmount.x + camera.transform.up * panAmount.y; 6 7 camera.transform.position += (direction * panSpeed * Time.deltaTime); 8 PositionPivot(); 9}
- The Pivot point is calculated by raycasting the
Cameraforward direction into aPlanedefined parallel to the ground, at theZeroposition.
1private void PositionPivot() 2{ 3 var distance = 0.0f; 4 5 var ray = new Ray(cameraTransform.position, cameraTransform.forward); 6 7 if (floorPlane.Raycast(ray, out distance)) 8 { 9 transform.position = ray.GetPoint(distance); 10 } 11}
Zoom View
- Zooming is easier, just moving the
Cameraalong itsforwarddirection.
1private void HandleZoom() 2{ 3 if (zoomAmount == 0.0f) { return; } 4 5 var direction = camera.transform.forward; 6 camera.transform.position += (direction * zoomAmount * Time.deltaTime); 7}
Orbit View
- Orbiting is easy thanks to the
RotateAroundhelper function from Unity. - We make the
Camerarotate around the pivot position, around the worldupdirection, and around therightdirection of the camera.
1private void HandleOrbit() 2{ 3 if (orbitAmount == Vector2.zero) { return; } 4 5 cameraTransform.RotateAround(transform.position, Vector3.up, -1.0f * orbitAmount.x * orbitSpeed * Time.deltaTime); 6 cameraTransform.RotateAround(transform.position, cameraTransform.right, orbitAmount.y * orbitSpeed * Time.deltaTime); 7}
GUIs for Playground
- A set of
GUIinputs to let you tweak values for the demo. - These can be hooked up via events to your objects and shaders, to showcase behavior.